


Electricity is a flow, or current, of electric charge, often in the form of electrons through a conductor, such as a metal wire. An electrical charge that has built up on an object but isn't moving is called static electricity.
Electrical energy can either be natural, such as from lightning and even electrical eels, or man-made, from an electrical generator. Since the 19th century, humans have used electricity to power many important parts of our lives, from lightbulbs to supercomputers.
AC/DC is an Australian rock band that was formed in the 1970s. The band's name comes from the two main types of electricity: direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC). DC electricity is like a one-way street where the electrons flow in only one direction, while AC electricity is like a two-way street where the electrons flow back and forth.
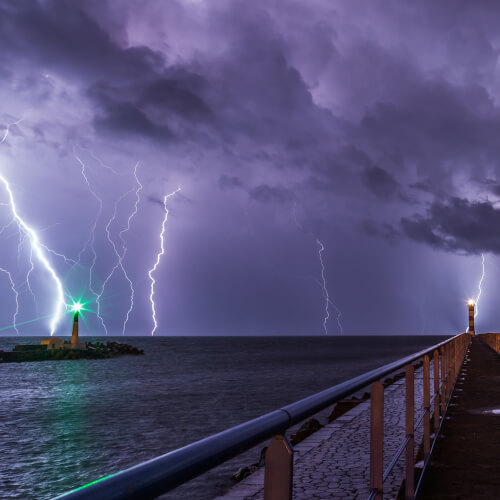
Lightning is a discharge of static electricity that often happens during thunderstorms. It forms when there is a buildup of electrical charges between a cloud and the ground or between two clouds. When the difference in charges becomes large enough, a bolt of lightning is created between the two, with a voltage of up to 300 million volts and temperature up to 30,000°C (54,000 °F). The surface of the Sun, on the other hand, is only about 5,600°C (10,000°F).
Electric eels are not actually eels, but a type of fish found in South America. They have three pairs of abdominal organs called electrocytes that can generate electricity for navigation, communication, and hunting. The voltage of their shocks depends on the situation, with low voltage shocks used for communication and higher voltage shocks used for stunning prey or defending themselves against predators. Some of their most powerful shocks are around 600 V, about 5 times the voltage of an electrical outlet in the US.
In 1800 Italian physicist and chemist Alessandro Volta invented the first battery, calling it the "voltaic pile." He created it by stacking alternating layers of zinc (Zn) and copper (Cu) discs separated by pieces of cardboard soaked in salt water. This created a chemical reaction that generated a steady flow of electricity. While today's batteries look quite different and are much more efficient, they still use the same basic ideas to store electricity.
Around 600 BC, the Greek philosopher Thales of Miletus discovered that rubbing fur on amber, or dried tree sap, would cause the amber to attract feathers and small pieces of paper. He named this phenomenon "elektron," which is the Greek word for amber.