


An atom is the basic building block of each of the 118 different chemical elements on the periodic table. Atoms are often found in nature as groups of two or more atoms, called molecules, held together in different chemical ways, called bonds.
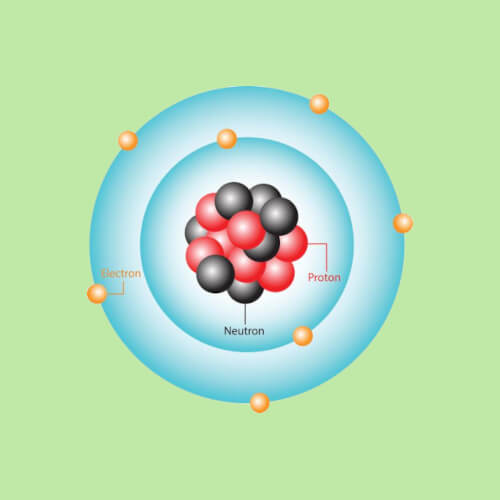
Atoms are made of even smaller components called subatomic particles, the term for all particles smaller than atoms. These include positively-charged protons, neutral neutrons, and negatively-charged electrons.
To get a better idea of what's going on with these subatomic particles, it helps to imagine an atom as a tiny solar system. In the center, there is a small, dense region called the nucleus containing protons and neutrons. Remember, protons have a positive charge and neutrons have no charge and are neutral. Most importantly, it's the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom that actually determines what element it is. For example, the nucleus of a hydrogen (H) atom has 1 proton, while a helium (He) atom has 2 protons. Atoms of oganesson (Og), element #118 on the periodic table, have 118 protons in their nuclei!
Outside the nucleus are the electrons, the significantly-smaller subatomic particles that carry negative electrical charge. Because they have opposite charge, the electrons are attracted to the positively charged protons in the nucleus. This causes them to zoom around the nucleus sort of like planets orbiting around the Sun. Their movement creates cloud-like regions surrounding the nucleus that scientists call "orbitals," or "shells."
Gold is a very malleable and ductile metal, meaning it can be hammered or stretched into thin sheets or wires. In fact, gold is so malleable that it can be beaten into sheets that are as thin as a single atom, which is about 0.3 nm (nanometers, or billionths of a meter) thick! These ultra-thin sheets of gold, called "monolayers," have unique optical and electronic properties that make them useful in a variety of applications, from electronics to medical devices.
Scanning tunneling microscopes (STMs) and atomic force microscopes (AFMs) are two types of instruments that allow scientists to "see" individual atoms and even manipulate them. These microscopes work by scanning a tiny probe over the surface of a sample and measuring the interactions between the probe and the atoms. By creating a 3D map of the interactions, scientists can create images of the surface with incredibly high resolution, sometimes even showing individual atoms.
Atoms are incredibly small, with a diameters measuring from 0.1 to 0.5 nm (nanometers, or billionths of a meter). To put that into perspective, a single strand of human hair is about 100,000 nm wide, which means you could fit anywhere from 200,000 to 1 million atoms side by side on the width of a single strand of hair!
The atoms in the elements that make up our bodies, such as carbon, oxygen, and iron, were formed in the hearts of massive stars that eventually exploded as supernovae. The intense heat and pressure of these explosions caused elements like hydrogen and helium to fuse together into heavier elements, which were then scattered into space. Over time, these elements eventually formed new stars and planets, including Earth.
While the number of atoms can vary greatly depending on a person's size, weight, and body composition, scientists have estimated that an average adult human body is made up of roughly 7 octillion (7 x 10^27), or 7 billion billion billion atoms. The vast majority of these atoms are hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon atoms, which are the primary building blocks of organic molecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
Put another way, if you were to magnify an atom to the size of a sports stadium, the nucleus would only be about the size of a pea! It's only because these particles are so small and so tightly packed together that we perceive them as solid objects.